Structural Trade-Offs in AI Server Rack Engineering
As AI server racks continue to evolve toward higher power density and modular deployment, frame design has become a critical engineering decision. One of the most common design trade-offs lies between load-bearing frames and lightweight frame structures.
Selecting the appropriate frame architecture affects not only mechanical strength, but also thermal management, scalability, installation efficiency, and long-term reliability. This guide compares both approaches and outlines practical considerations for AI infrastructure designers.
Load-Bearing Frame Design
Designed for strength, stability, and long-term structural integrity
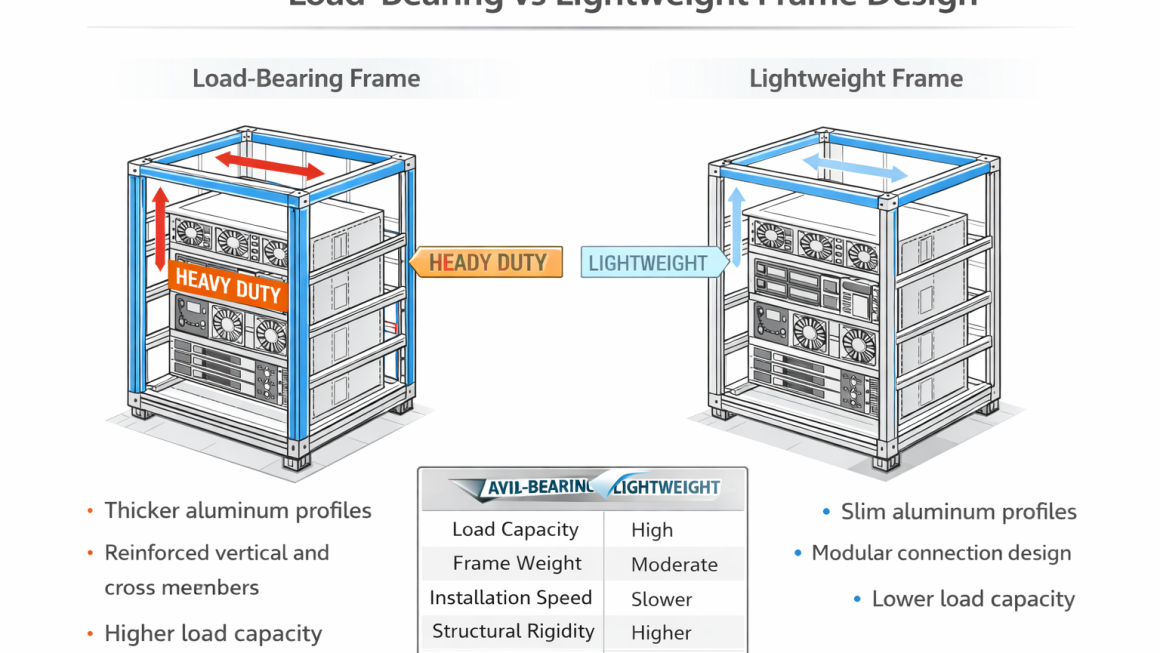
Load-bearing frames prioritize mechanical rigidity and high static load capacity. These structures are typically used in AI racks that support heavy server nodes, power modules, and liquid cooling components.
Key characteristics:
- Thicker aluminum profiles with higher moment of inertia
- Reinforced vertical columns and cross members
- Optimized for vertical and lateral load resistance
- Suitable for high rack density and long service life
Typical applications:
- High-performance AI training clusters
- Liquid-cooled server racks
- Permanent or semi-permanent data center installations
- Seismic or vibration-sensitive environments
Advantages:
- Excellent structural stability
- Reduced deformation under sustained load
- Better tolerance for uneven weight distribution
Trade-offs:
- Higher material cost
- Increased overall rack weight
- Longer assembly and transportation time
Lightweight Frame Design
Optimized for flexibility, speed, and modular deployment
Lightweight frame designs focus on minimizing material usage while maintaining sufficient structural integrity for typical server loads. This approach is increasingly popular in scalable and modular AI infrastructure.
Key characteristics:
- Slim aluminum profiles
- Reduced cross-section thickness
- Modular connection points
- Optimized for fast assembly and reconfiguration
Typical applications:
- Edge AI deployments
- Temporary or mobile data centers
- Modular AI test environments
- Cost-sensitive projects
Advantages:
- Lower material and shipping costs
- Faster installation and reconfiguration
- Easier handling during deployment
Trade-offs:
- Lower maximum load capacity
- More sensitive to vibration and long-span deflection
- May require additional reinforcement for expansion
Key Engineering Comparison
| Design Aspect | Load-Bearing Frame | Lightweight Frame |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | High | Moderate |
| Structural Rigidity | Excellent | Adequate |
| Weight | Higher | Lower |
| Installation Speed | Moderate | Fast |
| Scalability | Medium | High |
| Cost Efficiency | Medium | High |
Design Selection Considerations
When choosing between load-bearing and lightweight frame designs, engineers should evaluate:
- Server weight per rack unit
- Cooling method (air vs liquid)
- Expected expansion or reconfiguration
- Installation environment and vibration exposure
- Total cost of ownership over system lifespan
In many modern AI data centers, a hybrid approach is adopted—using load-bearing vertical columns combined with lightweight horizontal members to balance strength and flexibility.
There is no universal solution for AI server rack frame design. Load-bearing frames excel in high-density, long-term deployments, while lightweight frames offer speed and adaptability for modular systems.
A clear understanding of operational requirements and structural constraints is essential to selecting the optimal frame architecture.