In high-density AI hardware, aluminum frames are more than structural components—they directly interact with thermal systems, electrical interfaces, and environmental factors.
Surface treatments on aluminum are commonly used, but not all treatments are equally important in AI hardware. Some are cosmetic, while others are critical for performance, durability, and system reliability.
This article explores which aluminum surface treatments truly matter in AI systems, why they are applied, and how engineers can make informed choices.
1. Why Surface Treatments Are Important
Aluminum’s natural properties—lightweight, high thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance—make it ideal for AI racks. However, in high-performance environments, surface treatments serve several purposes:
- Corrosion Protection
- Even in controlled data center environments, moisture, humidity, and cleaning chemicals can cause corrosion over time.
- Protective layers extend frame life and maintain mechanical integrity.
- Electrical Isolation and Grounding
- Some treatments provide electrical insulation at contact points, while others improve conductive grounding across panels.
- Consistent electrical behavior is critical for sensitive AI electronics.
- Wear Resistance and Fatigue Mitigation
- Repeated insertion/removal of modules can wear untreated aluminum.
- Harder surfaces reduce micro-abrasion and fretting, lowering long-term fatigue risk.
- Thermal Interface Optimization
- Surface roughness affects contact resistance when aluminum interfaces with thermal pads or heat sinks.
- Controlled surfaces improve thermal path efficiency.
2. Common Surface Treatments and Their Relevance
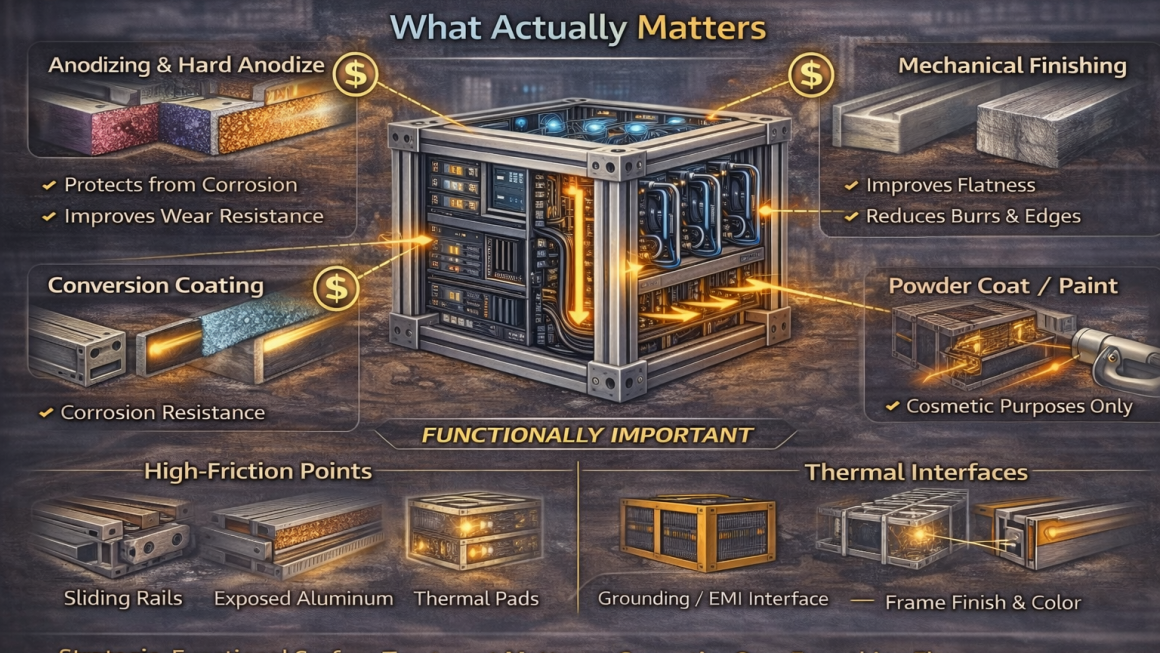
2.1 Anodizing
Description: Electrochemical oxidation creates a hard oxide layer.
Benefits:
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Increased surface hardness
- Can be dyed for aesthetic purposes (less relevant for AI racks)
AI Relevance:
- Protects from minor environmental exposure
- Reduces wear at high-contact points
- Minimal impact on thermal performance if thickness is controlled (<20 µm)
2.2 Hard Coatings (Hard Anodize / Ceramic Layers)
Description: Specialized anodizing produces thicker, denser, and harder surfaces.
Benefits:
- Higher abrasion resistance
- Better dimensional stability under cyclic load
- Surface electrical isolation in certain cases
AI Relevance:
- Ideal for rack rails, sliding components, and heavy module interfaces
- Slight increase in thermal resistance; must be accounted for in thermal design
2.3 Mechanical Finishing (Polishing, Sandblasting, Brushing)
Description: Alters surface texture without adding layers.
Benefits:
- Reduces burrs and sharp edges
- Improves flatness for thermal contacts
- Can enhance aesthetics for visible components
AI Relevance:
- Critical at thermal interface points to reduce micro-gaps
- Less important on hidden structural sections
2.4 Powder Coating / Paint
Description: Applied layer of polymer or epoxy on aluminum.
Benefits:
- Corrosion protection
- Cosmetic finish
AI Relevance:
- Mostly cosmetic in AI hardware, adds negligible thermal or mechanical benefit
- Avoid over-application where thermal contact is required
2.5 Conversion Coatings (Chromate / Non-Chromate)
Description: Thin chemical layers to improve corrosion resistance or adhesion of paint.
AI Relevance:
- Useful under powder coating or bonding surfaces
- Minor standalone benefits for bare aluminum exposed to controlled data center environments
3. Engineering Considerations for AI Applications
3.1 Thermal Implications
- Surface layers add thermal interface resistance
- Keep anodizing or coatings thin at thermal contact points (<10–20 µm)
- Roughness control improves contact conductance for thermal pads
3.2 Electrical Behavior
- Hard anodizing can electrically insulate surfaces
- Important when aluminum frames contact multiple grounding paths or EMI shields
- Unintended insulation may compromise grounding—engineers must plan surface treatment accordingly
3.3 Mechanical Integrity
- Hard coatings improve wear and fatigue resistance
- Mechanical finishing reduces stress risers
- Thick polymer coatings can create tolerance issues for tight module fits
4. Where Surface Treatments Actually Matter
- High-Friction Points
- Sliding rails, drawer interfaces, module mounts
- Use hard anodize or surface polishing to reduce wear and micro-movement
- Corrosion-Prone Exposed Areas
- Edges and open sections exposed to cleaning or humidity
- Thin anodize or conversion coatings sufficient
- Thermal Interfaces
- Heat sink mounting areas, thermal pads
- Keep surface flat and smooth, avoid thick coatings
- Grounding or EMI Interfaces
- Hard anodize may need selective removal or careful design
- Ensure continuity for electrical performance
5. Misconceptions to Avoid
- “Thicker coating = better performance” – Can impair thermal paths and tight tolerances
- “All surfaces need cosmetic finish” – Cosmetic coatings add cost without functional benefit
- “Any anodizing is enough for all mechanical stress points” – High wear areas need hard anodize or polished surfaces
6. Practical Recommendations for Engineers
- Use hard anodizing at wear-prone mechanical interfaces
- Keep thermal contact areas smooth and minimally coated
- Apply light protective anodizing to exposed structural areas
- Avoid thick polymer coatings where thermal or mechanical contact is needed
- Document surface treatment specifications for each critical frame interface
In AI hardware, aluminum surface treatment is about selective functional protection, not cosmetic perfection.
By understanding which treatments enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, thermal performance, and electrical behavior, engineers can:
- Extend rack and component lifespan
- Maintain thermal and mechanical performance
- Avoid unnecessary costs
The key takeaway:
In AI environments, strategic surface treatment is as important as the aluminum alloy itself. Treat only where it truly matters.